

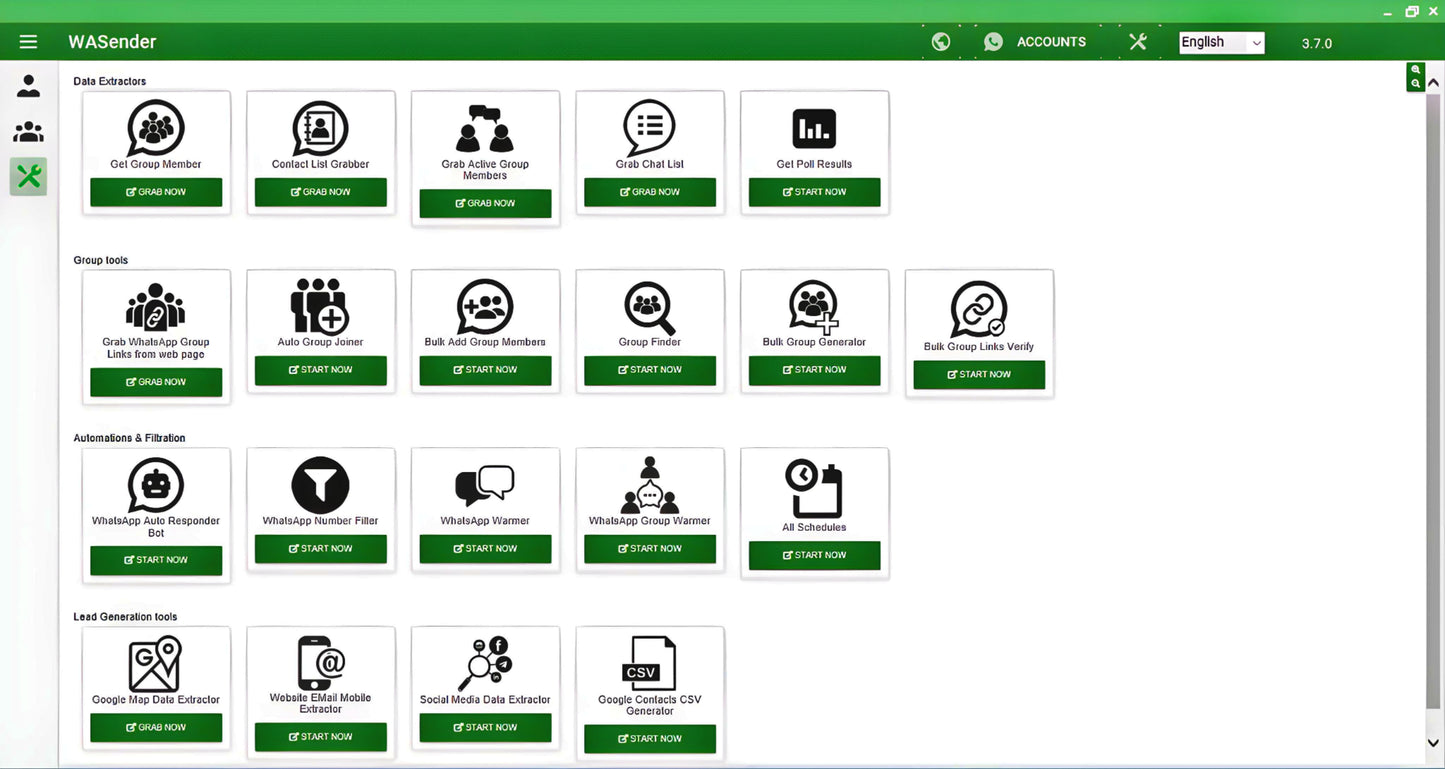
The WhatsApp Marketing Software is a powerful all‑in‑one software designed to help you automate messaging, extract data, generate leads, and manage WhatsApp activities with unmatched efficiency. Whether you're a marketer, business owner, or data collector, this software gives you everything you need — fast, reliable, and cost‑effective.
⚠️ Important Notice:
This software does not use the official WhatsApp API. It is an alternative automation solution. Because of this, there is a risk of WhatsApp account bans. However, we provide 8–10 expert steps that dramatically reduce the risk and help you operate safely and efficiently. You save massive API setup costs while enjoying more flexibility compared to official API tools.
Send Bulk Messages in One Click
-
Send personalized WhatsApp messages to hundreds of contacts instantly.
-
Supports formatting, media, emojis, and attachments.
-
Automates delivery without the need to message each person manually.
Grab Group Members
-
Extract member names and numbers from any WhatsApp group.
-
Perfect for outreach, marketing, or audience building.
Grab WhatsApp Group Links From Web
-
Automatically search and collect active WhatsApp group invite links from the internet.
-
Helps you discover targeted communities instantly.
WhatsApp Auto Bot
-
Automate custom replies, greetings, FAQs, and support messages.
-
Works 24/7 — even when you're offline.
Contact List Grabber
-
Fetch all saved contacts from your device or connected account.
-
Organizes them into clean lists for marketing or communication.
Google Map Data Extractor
-
Pull business details such as name, phone number, address, website directly from Google Maps.
-
Ideal for lead generation and local business targeting.
Auto Group Joiner
-
Automatically join WhatsApp groups using collected invite links.
-
Saves hours of manual effort.
WhatsApp Number Filter
-
Instantly check which phone numbers are active on WhatsApp.
-
Avoids bounce rates and preserves messaging credits.
Grab Active Group Members
-
Extract only active or recently engaged group members.
-
Helps build high‑quality, responsive contact lists.
Grab Chat List
-
Fetch your complete chat list with essential details.
-
Useful for sorting, archiving, cleanup, and analytics.
Bulk Add Group Members
-
Add multiple contacts to groups at once.
-
Saves time for admins and campaign managers.
Group Finder
-
Search and discover WhatsApp groups by keywords or categories.
-
Perfect for niche targeting.
Bulk Group Generator
-
Automatically create hundreds of groups.
-
Great for large communities, marketing campaigns, and segmentation.
Google Contacts CSV Generator
-
Export your contacts into a clean, Google‑friendly CSV format.
-
Makes backup, migration, and importing extremely easy.
Website Email & Mobile Extractor
-
Extract emails, phone numbers, and contact info from websites.
-
Essential for data collection and lead generation.
WhatsApp Warmer
-
Send low‑frequency automated messages to warm up new numbers.
-
Helps minimize bans and increase trust score.
Get Poll Results
-
Collect and analyze poll results from WhatsApp efficiently.
-
Useful for surveys, feedback, and fast decision‑making.
Social Media Data Extractor
-
Extract public data from major social media platforms.
-
Ideal for audience research and competitor analysis.
All Pakistan Phone Number Database
-
Access a categorized list of Pakistani phone numbers.
-
Super useful for local marketing and outreach.
⚠️ Safety & Ban Minimization
Using non‑API tools always carries a risk. However, your purchase includes:
A full 8–10 step guide to minimize the ban risk to a very, very low level.
Empower your WhatsApp workflow — save time, cut costs, and automate everything smartly.





